When it comes to building a reliable solar power system, properly wiring your battery bank is non-negotiable. Whether you’re powering a home, RV, or off-grid cabin, how your batteries are wired affects voltage and capacity in Amp-Hours (AH). It also impacts safety and performance.
In this post, you’ll learn:
✅ The difference between series, parallel, and series-parallel battery wiring
✅ How to safely connect batteries
✅ Wiring diagrams and tips for beginners
✅ Common mistakes to avoid
🔌 Why Do You Need to Wire Batteries Together?
A single battery often isn’t enough to store the energy your solar panels generate or supply the daily energy needed to power your loads. So, we connect multiple batteries to form a battery bank that can store more energy or work at higher voltages — or both.
Depending on your setup, you can:
- Increase voltage (e.g. from 12V to 24V or 48V) – Series connection
- Increase amp-hour capacity (for longer runtime) – Parallel connection
- Or both with a series-parallel configuration
Let’s break these down.
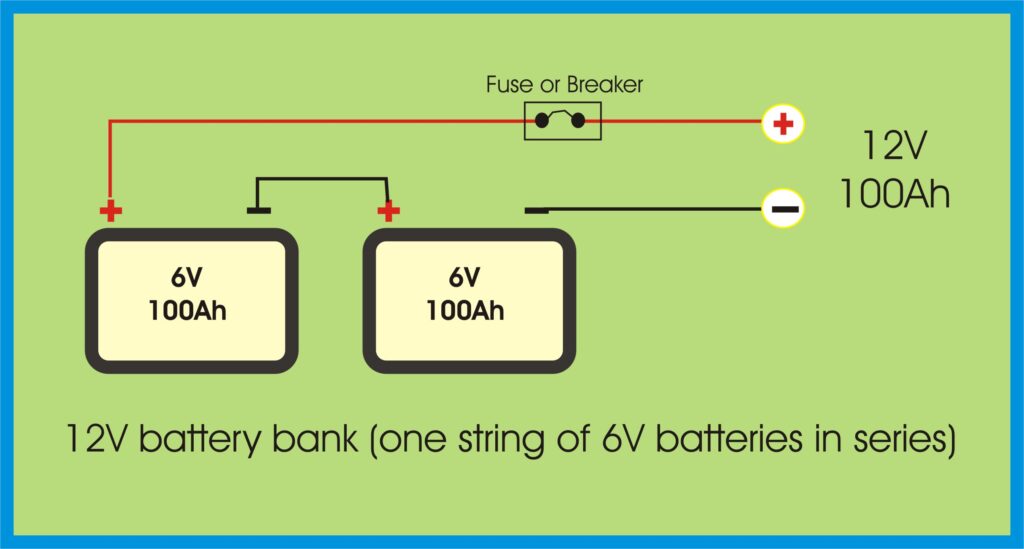
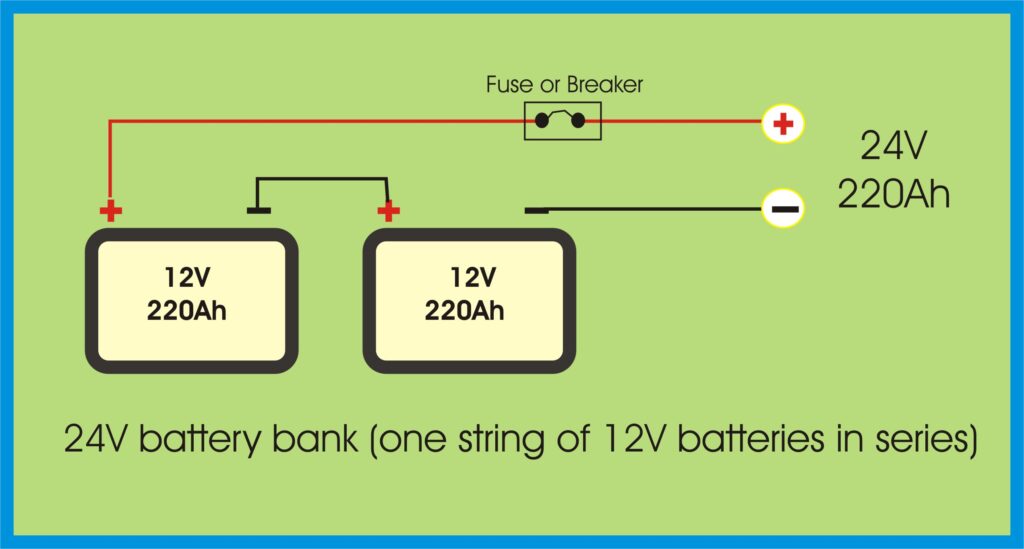
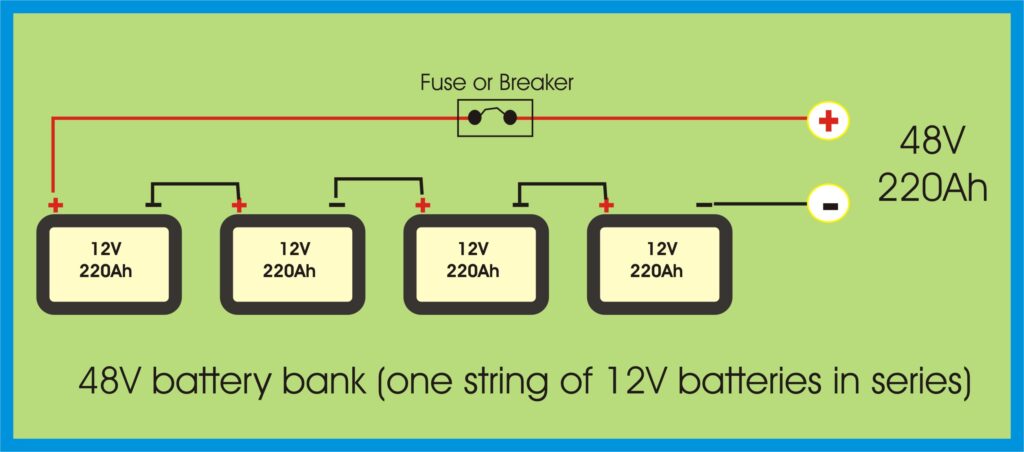
🔗 Series Connection – For Higher Voltage
In a series connection, you connect the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of the next.
What it does:
- Increases total voltage
- Keeps amp-hour (Ah) capacity the same
Example:
Four 12V 220Ah batteries in series = 48V 220Ah total
✅ Ideal for 48V inverters and reducing cable size
Wiring Diagram:
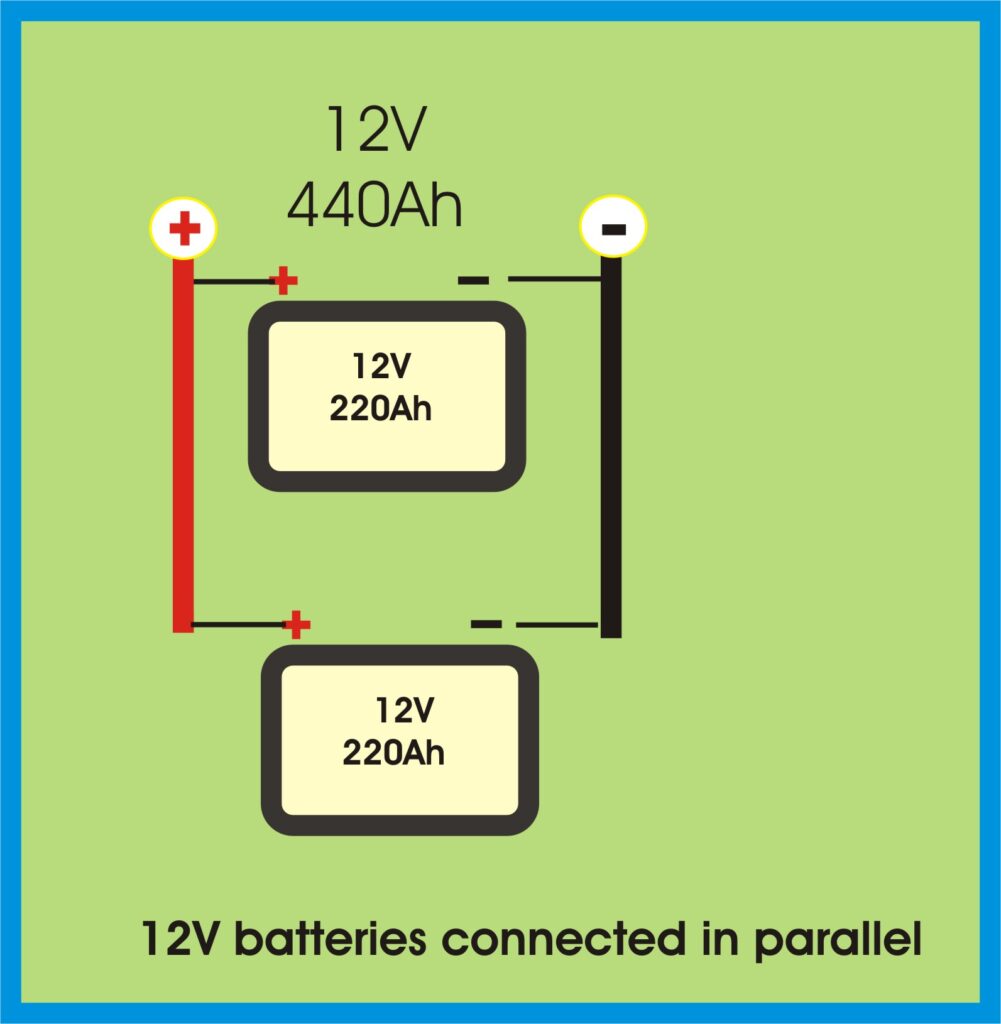
🔀 Parallel Connection – For More Capacity
In a parallel connection, you connect all positive terminals together and all negative terminals together.
What it does:
- Keeps voltage the same
- Increases total amp-hour (Ah) capacity
Example:
Two 12V 220Ah batteries in parallel = 12V 440Ah total
✅ Ideal for systems where low voltage but high capacity is needed
Wiring Diagram:
🔁 Series-Parallel – Best of Both Worlds
Need more voltage and more capacity? You can wire batteries in series-parallel.
Wiring diagram:
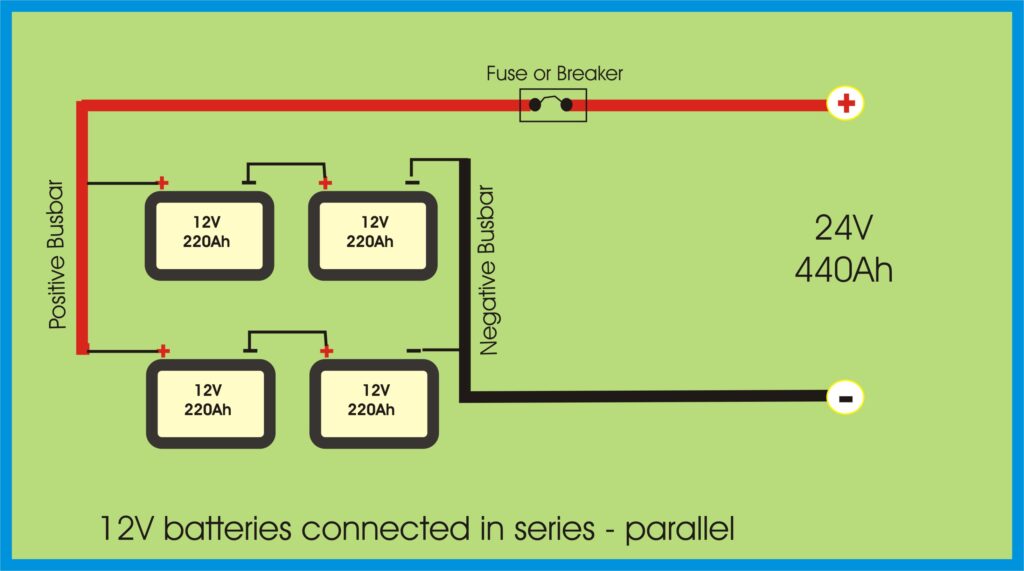
Wiring Tip:
Use identical batteries (same brand, age, voltage, and capacity) to prevent imbalance.
⚠️ Safety Tips for Wiring Battery Banks
- Double-check polarity. Reverse polarity can damage your equipment or cause fire.
- Use fuses or circuit breakers between connections, especially between the bank and the inverter.
- Ensure solid connections. Loose terminals cause resistance, heat, and voltage drop.
- Use proper cables. Thicker cables reduce voltage drop, especially in high-current systems.
- Don’t mix old and new batteries — it leads to uneven charging and faster wear.
🛠️ Pro tip: Use a battery balancer or BMS when wiring lithium batteries in series to ensure equal voltage across each cell.
🚫 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- ❌ Mixing different types or capacities of batteries
- ❌ Using too-thin cables for long runs
- ❌ Forgetting to fuse battery banks
- ❌ Skipping regular voltage checks
- ❌ Connecting batteries with corroded or dirty terminals
✅ Conclusion
Wiring your batteries correctly is foundational to a safe and efficient solar setup. Whether you’re going for higher voltage, more capacity, or both — understanding battery wiring gives you control over your system’s performance and lifespan.
Have questions about your setup? Drop them in the comments or send us a message — we’re here to help power your journey to energy independence! ⚡
📘 Want to Build the Perfect Solar System?
Struggling to size your solar panels, charge controller, batteries, cables, breakers or inverter the right way? 🔍
Grab my easy-to-follow PDF guide on Solar System Sizing — designed for beginners, installers, and DIY enthusiasts.
It covers:
- ✅ How to calculate your daily energy consumption
- ✅ How to size your battery bank
- ✅ How to size your solar panels, charge controller, breakers and fuses
- ✅ Inverter sizing
Leave a Reply